Cái tụ bù thì chỉ làm tăng cos @ ,giảm dòng điện A chứ có giảm công suất đâu mà tiết kiệm. Tiết kiệm là tiết kiệm cho ông điện lực không phải bù cos @. Giảm dòng thì dây điện đỡ nóng hơn tý , đỡ tổn hao tren dây có đáng kể gì đâu !
Cụ này nói chuẩn này, Vod cụ 1 ly.
Cái thiết bị đó nó làm tăng cos phi, qua đó giảm dòng điện nhưng công suất tiêu thụ điện vẫn không đổi nên hầu như không có tác dụng tiết kiệm điện khi dùng trong nhà dân. Dùng tụ bù hoặc thiết bị bọn nó quảng cáo tiết kiệm thực ra là tiết kiệm cho ông điện lực, tuy nhiên ở quy mô hộ gia đình thì cái tiết kiệm nà cũng chẳng đáng là bao
Thêm cho các cụ tham khảo bọn tây nó cũng nói về cái này rồi đó ợ:
http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/the-real-truth-behind-household-power-savers
A household power low voltage saving devices has recently received a lot of attention from both consumers and manufacturers. It is generally used in residential homes to save energy and to reduce electricity bills. It is a small device which is to be plugged in any of the AC sockets in the house (Mostly near Energy Meter). Moreover, some of the companies claim that their power savers save up to 40% of the energy.
Many people believe that the claims made by the power savers manufacturing companies are false. Almost all people who buy power savers do it to reduce their
electricity bills.
Many people who have used these power savers said that they could reduce their electricity bills with the devices; however the reduction was not as much as they had expected. Moreover, they could not figure out if the reduction in electricity bills was due to the power savers or because of their efforts to reduce their electrical usage. There have been several serious discussions about the genuineness of the device.
In this note, we will try to find the real truth behind these power savers which claim to save as much as 40% of energy.
Working Principle of Power Saver as per Manufacture
A Power Saver is a device which plugs in to power socket. Apparently just by keeping the device connected it will immediately reduce your power consumption. Typical claims are savings between 25% and 40%.
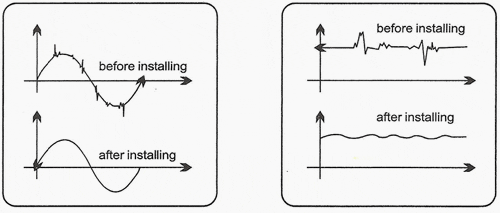
It is known that the electricity that comes to our homes is not stable in nature. There are many fluctuations, raise and falls, and surges/Spikes in this current. This unstable current cannot be used by any of the household appliances. Moreover, the fluctuating current wastes the electric current from the circuit by converting electrical energy into heat energy.
This heat energy not only gets wasted to the atmosphere, but also harms the appliances and wiring circuit.
Household power saver device - Schematic diagram
Power Saver stores the electricity inside of it using a system of capacitors and they release it in a smoother way to normal without the spikes. The systems also automatically remove carbon from the circuit which also encourages a smoother electrical flow. This means that we will have less power spikes. More of the electricity flowing around circuit can be used to power appliances than before.
Basically it is claimed that Power savers work on the principle of
surge protection technology. Power savers work on straightening this unstable electric current to provide a smooth and constant output. The fluctuation in voltage is unpredictable and cannot be controlled. However, the power savers utilize current fluctuation to provide a usable power by acting like a filter and allowing only smooth current to pass through the circuit. Power savers use capacitors for this purpose. When there is a surge of current in the circuit, the capacitor of the power saver stores the excess current and releases it when there is a sudden drop. Thus only smooth output current comes out of the device.
Moreover, a power saver also removes any type of carbon in the system, which facilitates further smoother flow. The main advantage of power savers is not that they provide a
backup system in times of low current, but that it protects the household appliances. It is known that a sudden rise in the power can destroy the electrical appliance. Thus, the power saver not only protects the appliance but also increases its life. Moreover, they also reduce the energy consumption and thus the electricity bills.
The amount of power saved by a power saver depends on the number of appliances on the electrical circuit. Also, the system takes at least a week to adapt itself fully to the circuit, before it starts showing its peak performance. The maximum amount of voltage savings will be seen in areas where in the current fluctuation is the highest.
Household Power Saver Scam Review
Power Factor Correction for residential customers (home owners) is a scam? At most, each unit is worth as an investment. Power factor correction does make sense for some commercial / industrial customers.
Many companies are promoting and advertise that their Power Saver unit are able to save domestic residential power consumption by employing an
“active power factor correction” method on the supply line. The concept seems pretty impressive as the concept is true and legally accepted. But practically, we will find that it’s not feasible.
To support above statement first we need to understand three terms:
- Type of electrical load of house,
- Basic power terminology (KW, KVA, KVAR).
- Electrical tariff method of electricity company for household consumer and industrial consumer.
There are basically two kinds of load that exists in every house: one that is resistive like incandescent lamps, heaters etc. and the other that’s capacitive or inductive like ACs, refrigerators, computers, etc.
The power factor of a Resistive Load like toaster or ordinary incandescent light bulb is 1 (one). Devices with coils or capacitors (like pumps, fans and florescent light bulb ballasts)-Reactive Load have power factors less than one. When the power factor is less than 1, the current and voltage are out of phase. This is due to energy being stored and released into inductors (motor coil) or capacitors on every AC cycle (usually 50 or 60 times per second).
There are three terms need to be understand when dealing with alternating (AC) power.
- First Term is kilowatt (kW) and it represents Real power. Real power can perform work. Utility meters on the side of House measure this quantity (Real Power) and Power Company charge for it.
- The second term is reactive power, measured in KVAR. Unlike kW, it cannot perform work. Residential customers do not pay for KVAR, and utility meters on houses do not record it too.
- The third term is apparent power, referred to as KVA. By use of multi meters we can measure current and voltage and then multiply the readings together we get apparent power in VA.
Power triangle
Power Factor = Real Power (Watts) / Apparent Power (VA)
Therefore,
Real Power (Watts) = Apparent Power × PF =
Voltage × Ampere × PF.
Ideally a
PF = 1, or unity, for an appliance defines a clean and a desired power consumption mostly Household Equipments (The dissipated output power becomes equal to the applied input power).
In the above formula we can see that if PF is less than 1, the amperes (current consumption) of the appliances increase, and vice verse.
With AC Resistive Load, the voltage is always in phase with the current and constitutes an ideal power factor equal to 1. However, with inductive or capacitive loads, the current waveform lags behind the voltage waveform and is not in tandem. This happens due to the inherent properties of these devices to store and release energy with the changing AC waveform, and this causes an overall distorted wave form, lowering the net PF of the appliance.
Manufacture claim that the above problem may be solved by installing a well-calculated inductor/capacitor network and switching it automatically and appropriately to correct these fluctuations. A power saver unit is designed exactly for this purpose. This correction is able to bring the level of PF very close to unity, thus improving the apparent power to a great extent.
An improved apparent power would mean less CURRENT consumption by all the domestic appliances.
So far everything looks fine, but what’s the use of the above correction?
The Utility Bill Which We pay is never based on Apparent Power (KVA) but it is based on Real Power (KW). The utility bill that we pay is never for the Apparent Power- it’s for the Real Power.
By Reducing Current Consumption Does Not Reduce Power Bills of Household Consumer.
Study of Power Saver in Domestic Load
Let us try to study Household’s Reactive-Resistive Electrical Load and Voltage Spike Characteristic by example.
1. Power Saver in Reactive Load of Home
Let’s take One Example for reactive Load: A refrigerator having a rated Real Power of 100 watts at 220 V AC has a PF = 0.6. So Power=Volt X Ampere X P.F becomes 100 = 220 × A × 0.6 Therefore, A = 0.75 Ampere
Now suppose after Installing Power Saver if the PF is brought to about 0.9, the above result will now show as: 100 = 220 × A × 0.9 And A = 0.5 Ampere
In the second expression we clearly show that a reduction in current consumption by the refrigerator, but interestingly in both the above cases, the
Real Power remains the same, i.e. the refrigerator continues to consume
100 watts, and therefore the utility bill remains the same. This simply proves that although the PF correction done by an energy saver may decrease the Amperage of the appliances,
it can never bring down their power consumption and the electric Bill amount.
Reactive power is not a problem for a Reactive Load of Home appliances like A.C, Freeze, motor for its operation.
It is a problem for the electric utility company when they charge for KW only. If two customers both use the same amount of real energy but one has a power factor of 0.5, then that customer also draws double the current. This increased current requires the Power Company to use larger transformers, wiring and related equipment.
To recover these costs Power Company charged a Penalty to industrial customers for their Low power factors and give them benefits if they improve their Power Factor in.
Residential customers (homes) are never charged extra for their reactive Power.
2. Power Saver in Resistive Load of Home
Since a resistive load does not carry a PF so there is not any issue regarding filtering of Voltage and Current, So Power = Voltage X Current.
3. In Voltage Spike / Fluctuation condition of Household Appliances
In above discussion simply proves that as long as the voltage and the current are constant, the consumed power will also be constant. However, if there’s any rise in the input voltage because of a fluctuation, then as explained above your appliances will be forced to consume a proportionate amount of power. This becomes more apparent because current, being a function of voltage, also rises proportionately. However, this rise in the power consumption will be negligibly small; the following simple math will prove this.
Consider a bulb consuming 100 watts of power at 220 volts. This simply means at 240 volts it will use up about 109 watts of power. The rise is just of around 9% and since such fluctuations are pretty seldom, this value may be furthermore reduced to less than 1%, and that is negligible.
Thus the above discussions convincingly prove that energy savers can never work and the concept is not practically feasible.
What happens when Power Saver is installed?
The Fig shows the result of using Power Saver. The air conditioner (which has a large compressor motor) is still consuming reactive power but it is being supplied by a nearby capacitor (which is what is in those “KVAR” boxes). If you were to mount it at the air conditioner and switch it on with the air conditioner plus you sized the capacitor perfectly, then there would be no reactive power on the line going back to the fuse panel.
If the wire between your fuse panels is very long and undersized, reducing the current would result in it running cooler and having a higher voltage at the air conditioner. These savings due to cooler wiring is minimal.
What happens when Power Saver is installed
A further complication is that if you install the “KVAR” unit at the fuse panel, it does nothing for the heat losses except for the two feet of huge wire between the fuse panel and the utility meter. Many KVAR units are marketed as boxes that you install at a single location.
If your power factor box is too large, then it will be providing reactive power for something else, perhaps your neighbor.
Top
Conclusion
Power factor correction devices improve power quality but do not generally improve energy efficiency (
meaning they would not reduce your energy bill). There are several reasons why their energy efficiency claims could be exaggerated.
First, residential customers are not charged for
KVA – hour usage, but by kilowatt-hour usage. This means that any savings in energy demand will not directly result in lowering a residential user’s utility bill.
Second, the only potential for real power savings would occur if the product were only put near in the circuit while a reactive load (such as a motor) were running, and taken out of the circuit when the motor is not running. This is impractical, given that there are several motors in a typical home that can come on at any time (refrigerator, air conditioner, HVAC blower, vacuum cleaner, etc.), but the Power Saver itself is intended for permanent, unattended connection near the house breaker panel.
And certainly not in the way the manufacturers recommend that they be installed, that is, permanently connecting them at the main panel. Doing that drags the power factor capacitive when the inductive motors are off and could create some real problems with ringing voltages.
The KVAR needs to be sized perfectly to balance the inductive loads. Since our motors cycle on and off and we don’t use the air conditioner in the winter, there is no way to get it sized properly unless we have something to monitor the line and switch it on and off capacity (capacitors) as necessary.
Adding a capacitor can increase the line voltage to dangerous levels because it interacts with the incoming power transmission lines. Adding a capacitor to a line that has harmonic frequencies (created by some electronic equipment) on it can result in unwanted resonance and high currents.
For commercial facilities, power factor correction will rarely be cost-effective based on energy savings alone. The bulk of cost savings power factor correction can offer is in the form of
avoided utility charges for low power factor.
Energy savings are usually below 1% and always below 3% of load, the higher percentage occurring where motors are a large fraction of the overall load of a facility. Energy savings alone do not make an installation cost effective.